- A robust vulnerability management system (VMS) helps organisations proactively identify, assess, and remediate security vulnerabilities.
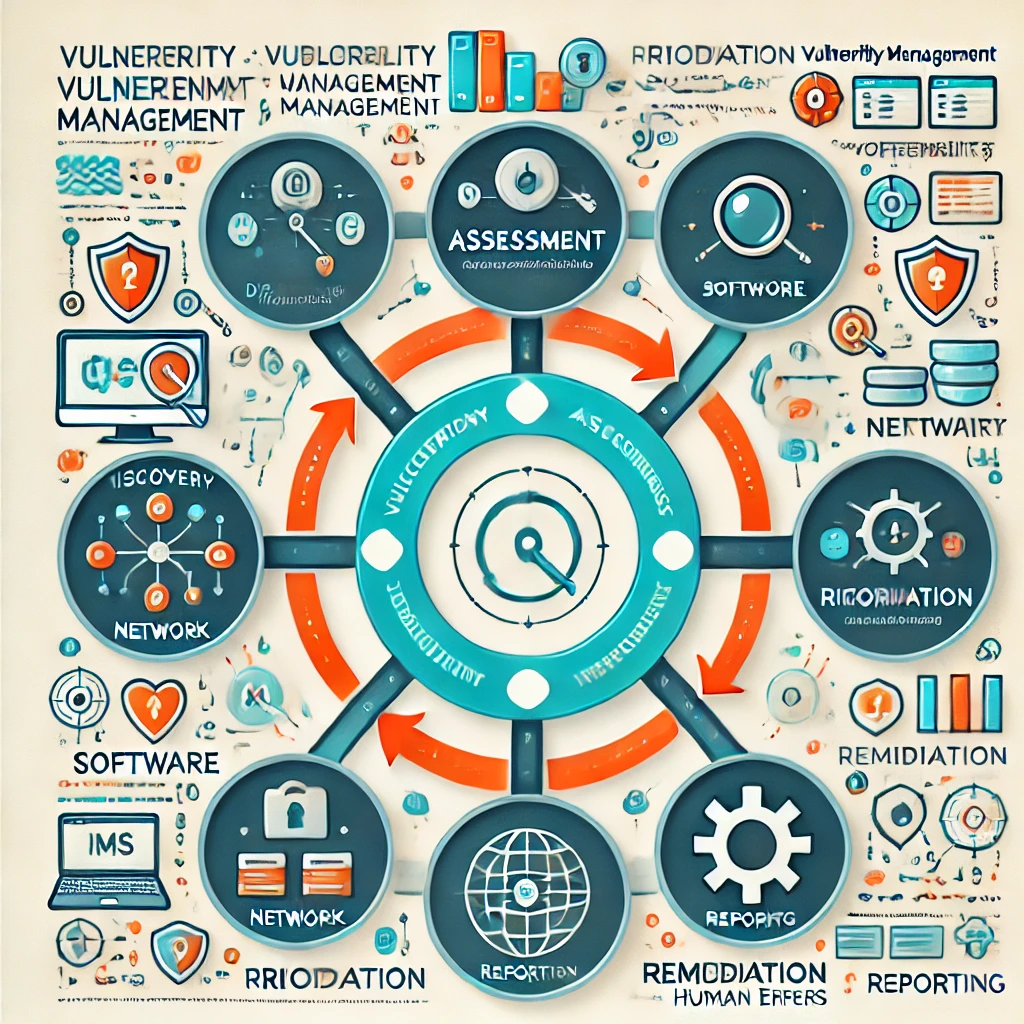
- Vulnerability management involves a systematic approach including identification, evaluation, remediation, and reporting.
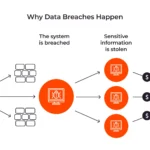
Vulnerabilities are inevitable in any digital landscape, but the way organisations handle them can make the difference between a minor hiccup and a catastrophic breach. Enter the vulnerability management system (VMS) — a structured approach to securing IT environments by proactively managing risks. It’s about understanding their potential impact and addressing them before they can be exploited.
What is a vulnerability management system?
A vulnerability management system (VMS) is a comprehensive framework designed to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate security vulnerabilities within an organisation’s IT infrastructure. This system ensures that any weak points in the network, software, or hardware are discovered and addressed before malicious actors can exploit them. VMS integrates various tools and processes, forming a continuous loop that keeps an organisation’s digital assets secure.
1. Identification: The first step involves scanning and identifying vulnerabilities within the system. Automated tools, such as network scanners and vulnerability assessment tools, are commonly used to detect weaknesses. These can range from outdated software, misconfigurations, to missing security patches.
2. Assessment and prioritisation: Once vulnerabilities are identified, they are assessed for potential impact. This involves analysing the severity of each vulnerability and its likelihood of being exploited. Vulnerabilities are then prioritised based on their risk level, ensuring that the most critical issues are addressed first.
3. Remediation: The next step is to mitigate the identified vulnerabilities. This could involve patching software, reconfiguring systems, or implementing additional security measures. Automation plays a significant role here, as it allows for rapid response and reduces the chance of human error.
4. Continuous monitoring: Vulnerability management is not a one-time task but a continuous process. Systems need to be regularly monitored for new vulnerabilities, and previously identified vulnerabilities need to be re-evaluated to ensure they have been effectively mitigated. Continuous monitoring also helps in quickly adapting to new threats and changes in the IT environment.
Also read: The backbone of digital infrastructure: Server management
Also read: Understanding vulnerability scanning: Key processes and types
Types of vulnerability management
1. Network-based vulnerability management: Focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure, including routers, firewalls, and other network devices. Regular network scans are conducted to ensure that the infrastructure is secure and free from potential entry points for attackers.
2. Host-based vulnerability management: Concentrates on individual hosts, such as servers and workstations. This type of management includes checking for vulnerabilities at the operating system and application levels, ensuring that all software is up-to-date and configured securely.
3. Application-based vulnerability management: Targets vulnerabilities within specific applications. This includes web applications, databases, and other software critical to business operations. Regular security assessments and code reviews are performed to identify and fix vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.